Polar amino acids play a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins, which are essential molecules in all living organisms. These amino acids contain functional groups that are hydrophilic, meaning they interact well with water molecules. This property allows polar amino acids to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules, influencing the overall shape and stability of proteins. Understanding the characteristics and functions of polar amino acids is key to unraveling the complexities of biochemistry.
When it comes to protein structure, polar amino acids contribute to the formation of specific regions within a protein molecule. These regions, known as polar pockets, provide binding sites for other molecules such as substrates or cofactors. By interacting with these polar pockets, molecules can undergo chemical reactions or signal transduction processes that are essential for various biological functions. The presence of polar amino acids in these binding sites ensures the specificity and efficiency of these interactions.
In addition to their role in protein structure, polar amino acids also play a significant role in the overall stability of proteins. The interactions between polar amino acids and water molecules help to maintain the solubility of proteins in aqueous environments. This is crucial for the proper folding of proteins into their functional three-dimensional structures. Without the presence of polar amino acids, proteins may not be able to maintain their native conformation, leading to loss of function and potentially harmful effects on cellular processes.
What are the Different Types of Polar Amino Acids?
There are several types of polar amino acids that are commonly found in proteins. These include:
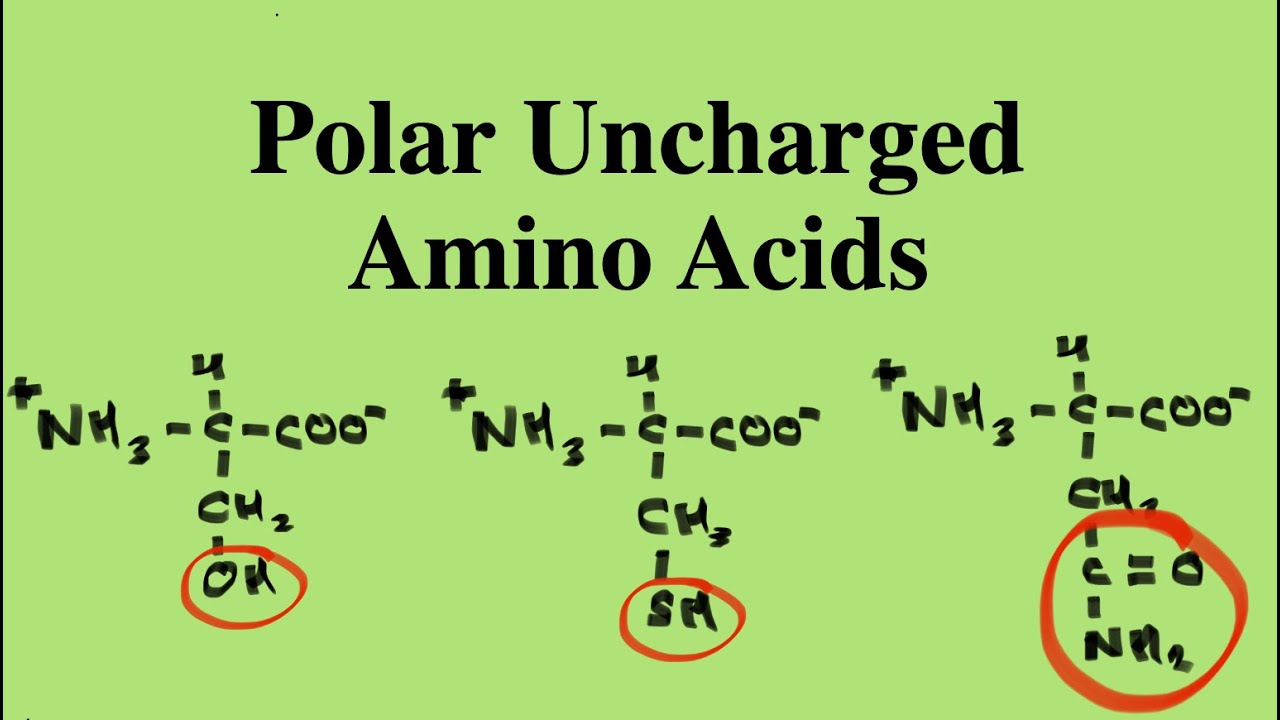
- Asparagine
- Glutamine
- Serine
- Threonine
How Do Polar Amino Acids Differ from Nonpolar Amino Acids?
One key difference between polar and nonpolar amino acids lies in their side chain properties. While nonpolar amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that are repelled by water, polar amino acids have hydrophilic side chains that interact favorably with water molecules. This difference in side chain characteristics influences the overall structure and function of proteins in significant ways.
Why are Polar Amino Acids Important for Enzyme Function?
Enzymes, which are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms, often contain polar amino acids in their active sites. These polar amino acids help to stabilize substrates and transition states during enzymatic reactions, increasing the efficiency and specificity of the reaction. Without the presence of polar amino acids, enzymes may not be able to perform their catalytic functions effectively.
How Do Polar Amino Acids Contribute to Protein Folding?
Protein folding is a complex process that involves the precise arrangement of amino acids to form a functional three-dimensional structure. Polar amino acids play a critical role in this process by forming hydrogen bonds with other amino acids, stabilizing secondary structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets. These interactions help to guide the folding of the protein into its native conformation, ensuring proper function within the cellular environment.
What Happens When Polar Amino Acids are Mutated?
Mutations in polar amino acids can have significant effects on protein structure and function. Depending on the nature of the mutation, the stability of the protein may be compromised, leading to misfolding and aggregation. This can result in the loss of protein function or the acquisition of new, potentially harmful functions. Understanding the impact of polar amino acid mutations is essential for studying genetic diseases and developing targeted therapies.
Can Polar Amino Acids Serve as Signaling Molecules?
Some polar amino acids, such as serine and threonine, can serve as phosphorylation sites in signaling pathways. Phosphorylation is a common post-translational modification that regulates protein activity and function in response to external stimuli. By adding phosphate groups to polar amino acids, cells can modulate the activity of key signaling proteins, influencing processes such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Understanding Horizontal Ridges On Fingernails
Exploring The Art Of Taking The Drill
Exploring The Enigmatic World Of Kafka

PPT Chapter 17 Amino Acids and Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free

What Are Polar Amino Acids? The Amino Company
How to remember the Polar Uncharged Amino Acids? MCAT Biochemistry