Respiratory arrest is a life-threatening medical emergency that occurs when a person's breathing stops. This can happen suddenly and without warning, leading to a lack of oxygen in the body. When oxygen levels drop, it can have serious consequences for the brain and other vital organs. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of respiratory arrest is crucial for prompt intervention and potentially saving a life.
In many cases, respiratory arrest is caused by a problem with the airway, lungs, or respiratory muscles. Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or choking can all lead to difficulty breathing and, if left untreated, may progress to respiratory arrest. Other factors such as drug overdose, drowning, or severe trauma can also result in respiratory failure. Recognizing the signs of respiratory distress is essential for early detection and intervention.
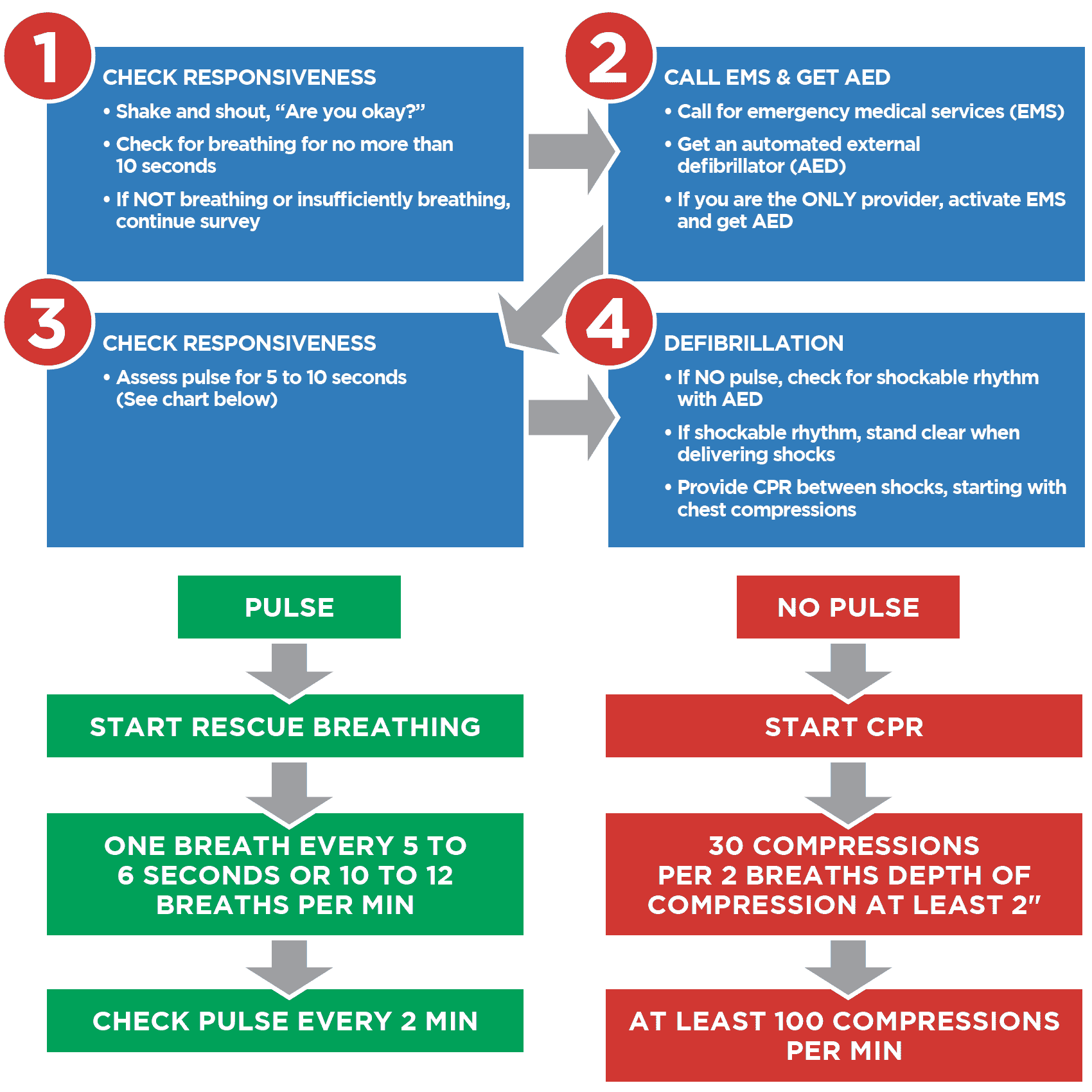
Common symptoms of respiratory arrest include gasping for air, shallow breathing, blue lips or fingertips, and loss of consciousness. If you suspect someone is experiencing respiratory distress, it is crucial to act quickly. Call emergency services immediately and begin administering CPR if the person is unresponsive. Prompt medical attention is essential to restore breathing and prevent further complications.
What are the Risk Factors for Respiratory Arrest?
Several factors can increase the risk of respiratory arrest, including:
- Chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD
- Obesity
- Drug overdose
- Trauma to the chest or airway
How is Respiratory Arrest Diagnosed?
Diagnosing respiratory arrest typically involves assessing the patient's breathing, oxygen levels, and overall clinical condition. Healthcare providers may perform a physical examination, order blood tests, chest X-rays, or other diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of respiratory failure.
What Treatment Options are Available for Respiratory Arrest?
The treatment for respiratory arrest depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In most cases, immediate intervention is necessary to restore breathing and oxygenation. This may involve interventions such as:
- Administering oxygen therapy
- Intubation and mechanical ventilation
- CPR and chest compressions
- Medications to support respiratory function
Can Respiratory Arrest be Prevented?
While some cases of respiratory arrest may be unavoidable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk. Managing chronic health conditions, avoiding drug abuse, and practicing safety measures to prevent accidents can all help lower the likelihood of respiratory failure.
What is the Prognosis for Respiratory Arrest?
The outlook for individuals who experience respiratory arrest depends on the underlying cause, promptness of intervention, and overall health status. Early recognition and treatment can significantly improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
When to Seek Medical Help for Respiratory Distress?
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of respiratory arrest, such as difficulty breathing or gasping for air, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. Delay in treatment can have serious consequences, so never hesitate to call for help in a respiratory emergency.
Exploring The Impact Of Putting A Fuel Filter Back With
Exploring The Option To Weigh Yourself At Walmart
Creswell Qualitative Research: Exploring The Depths Of Qualitative Inquiry

Understanding and Managing Respiratory Arrest CareerCert
ACLS Cases Respiratory Arrest ACLS Online Handbook
/adult-resuscitation-136811270-5a244663845b340036078f78.jpg)
Differences Between Respiratory and Cardiac Arrest