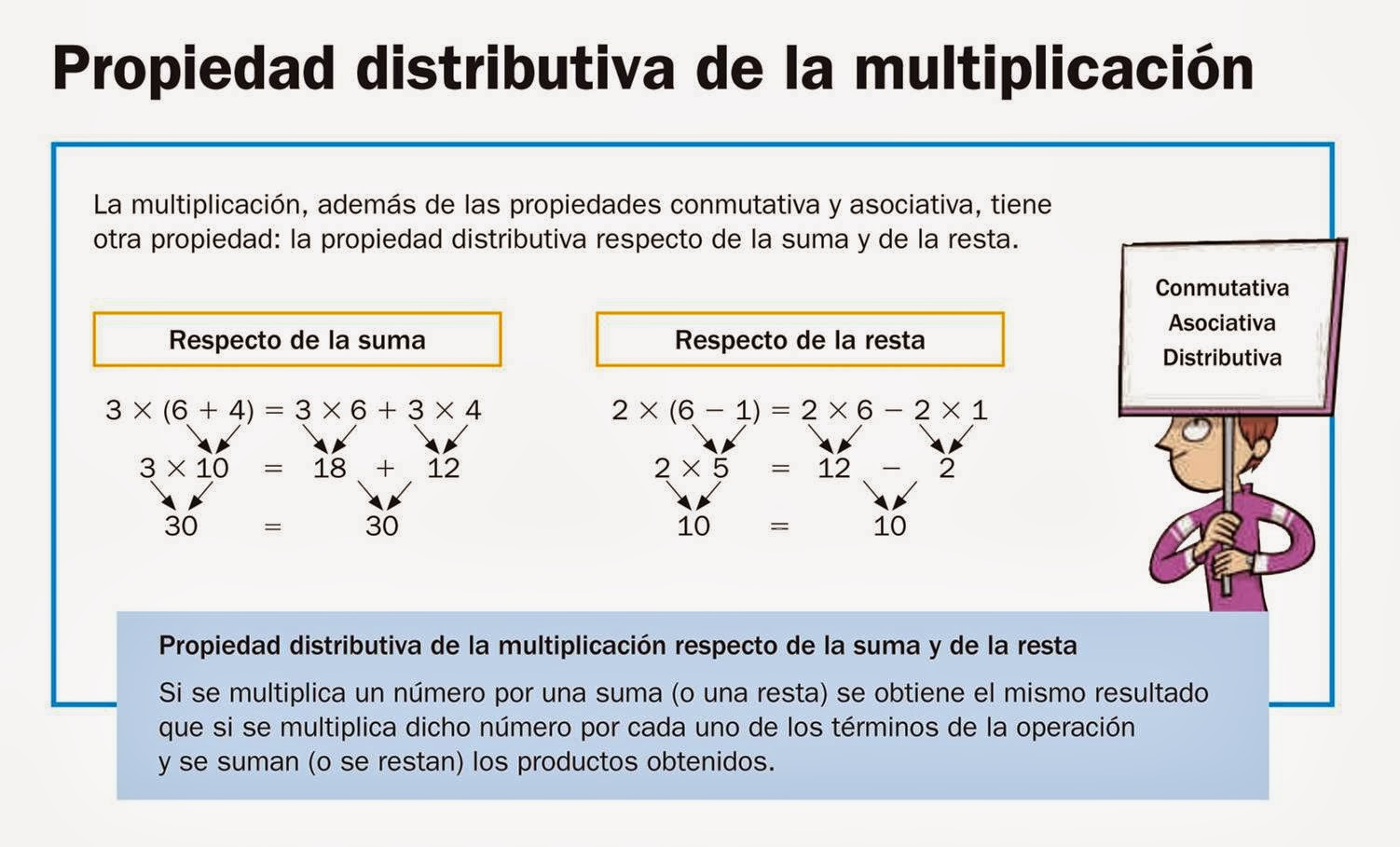
When it comes to understanding mathematical operations, the distributive property of multiplication is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in simplifying equations and expressions. In this article, we will explore various examples of how the distributive property of multiplication works, providing clarity and insight into this essential mathematical principle.
Before delving into specific examples, it is important to grasp the basic definition of the distributive property of multiplication. This property states that when you multiply a number by the sum of two other numbers, it is the same as doing each multiplication separately and then adding the results together. In simpler terms, it allows you to distribute the multiplication over addition, making calculations more manageable and efficient.
By applying the distributive property of multiplication, you can simplify complex expressions and equations, making them easier to solve. This property is a powerful tool in algebra and arithmetic, enabling you to break down complicated mathematical problems into simpler steps. Now, let's explore some examples to illustrate how the distributive property works in action.
How does the Distributive Property of Multiplication Work?
Example 1: Distributing Multiplication Over Addition
Let's consider the expression: 3 * (4 + 2). To apply the distributive property, we need to multiply 3 by each term inside the parentheses and then add the results together:
- 3 * 4 = 12
- 3 * 2 = 6
Now, add the results: 12 + 6 = 18. Therefore, 3 * (4 + 2) = 18. This example demonstrates how the distributive property allows us to simplify the multiplication of a number by the sum of two other numbers.
Example 2: Using the Distributive Property in Equations
Consider the equation: 2 * (x + 5). To simplify this equation using the distributive property, we multiply 2 by each term inside the parentheses:
- 2 * x = 2x
- 2 * 5 = 10
Therefore, 2 * (x + 5) simplifies to 2x + 10. By applying the distributive property, we can break down the equation into individual multiplications and additions, making it more straightforward to solve.
Why is the Distributive Property Important in Mathematics?
Example 3: Applying the Distributive Property to Variables
Let's examine the expression: a * (b + c). By distributing the multiplication over addition, we get:
- a * b = ab
- a * c = ac
Therefore, a * (b + c) simplifies to ab + ac. This example illustrates how the distributive property is crucial in algebra when working with variables and unknown quantities.
How can the Distributive Property Help Simplify Complex Equations?
Example 4: Using the Distributive Property with Negative Numbers
Consider the expression: -3 * (2 + 4). By applying the distributive property, we multiply -3 by each term inside the parentheses:
- -3 * 2 = -6
- -3 * 4 = -12
Adding the results gives us -6 + (-12) = -18. Therefore, -3 * (2 + 4) simplifies to -18. This example demonstrates how the distributive property can handle operations with negative numbers efficiently.
Exploring More Examples of the Distributive Property
By now, you have gained a better understanding of how the distributive property of multiplication works and its significance in simplifying mathematical expressions. Practice applying this property to various equations and problems to strengthen your skills in algebra and arithmetic. Remember, mastering the distributive property will enhance your problem-solving abilities and pave the way for tackling more advanced mathematical concepts with confidence.
Celebrating Happy Three Kings Day
Understanding AFR: A Comprehensive Guide
Cuantas Calorias Se Deben Consumir Al Dia Segun La Edad

Propiedad distributiva explicación, ejemplos y ejercicios resueltos
Ejemplos De Propiedad Distributiva En La Multiplicación Nuevo Ejemplo
propiedades de la multiplicacion